Reducing pediatric RSV burden is top priority
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Prevention or early effective treatment of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in infants and small children holds the promise of sharply reduced burdens of both acute otitis media (AOM) and pneumonia, Terho Heikkinen, MD, PhD, predicted in the Bill Marshall Award Lecture presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases (ESPID).
RSV is by far the hottest virus in the world,” declared Dr. Heikkinen, professor of pediatrics at the University of Turku (Finland).
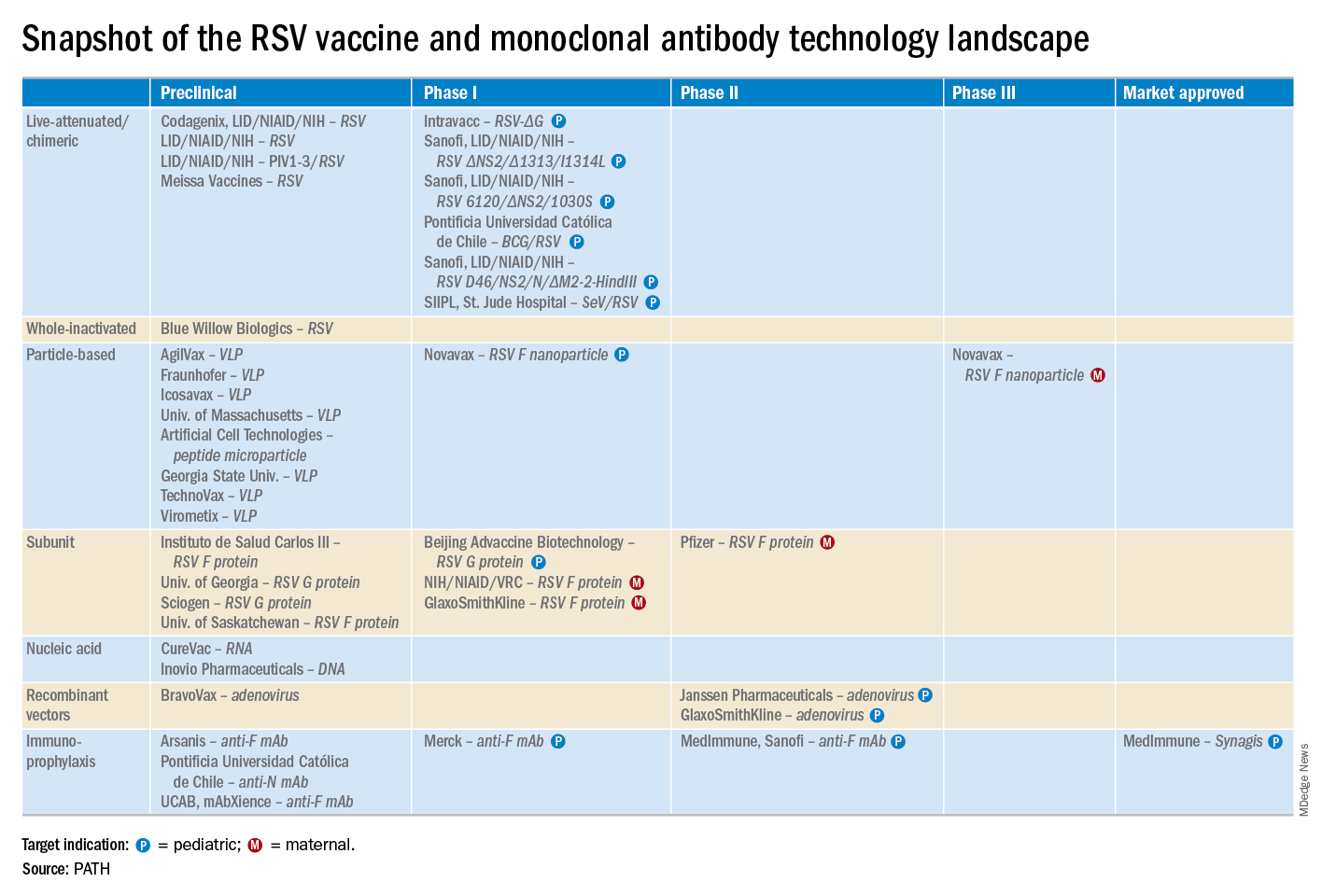
“A lot of progress is being made with respect to RSV. This increased understanding holds great promise for new interventions,” he explained. “Lots of different types of vaccines are being developed, monoclonal antibodies, antivirals. So
Today influenza is the only respiratory viral infection that’s preventable via vaccine or effectively treatable using antiviral drugs. That situation has to change, as Dr. Heikkinen demonstrated early in his career; RSV is the respiratory virus that’s most likely to invade the middle ear during AOM. It’s much more ototropic than influenza, parainfluenza, enteroviruses, or adenoviruses (N Engl J Med. 1999 Jan 28;340[4]:260-4), he noted.
The Bill Marshall Award and Lecture, ESPID’s most prestigious award, is given annually to an individual recognized as having significantly advanced the field of pediatric infectious diseases. Dr. Heikkinen was singled out for his decades of work establishing that viruses, including RSV, play a key role in AOM, which had traditionally been regarded as a bacterial infection. He and his coinvestigators demonstrated that in about two-thirds of cases, AOM is actually caused by a combination of bacteria and viruses, which explains why patients’ clinical response to antibiotic therapy for AOM often is poor. They also described the chain of events whereby viral infection of the upper airway epithelium triggers an inflammatory response in the nasopharynx, with resultant Eustachian tube dysfunction and negative middle ear pressure, which in turn encourages microbial invasion of the middle ear. Moreover, they showed that the peak incidence of AOM isn’t on day 1 after onset of upper respiratory infection symptoms, but on day 3 or 4.
“What this tells us is that, once a child has a viral respiratory infection, there is a certain window of opportunity to try to prevent the development of the complication if we have the right tools in place,” Dr. Heikkinen said.
He and his colleagues put this lesson to good use nearly a decade ago in a randomized, double-blind trial in which they showed that giving oseltamivir (Tamiflu) within 12 hours after onset of influenza symptoms in children aged 1-3 years reduced the subsequent incidence of AOM by 85%, compared with placebo (Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Oct 15;51[8]:887-94).
Maternal immunization protects against serious RSV infection in infancy
These observations paved the way for the ongoing intensive research effort exploring ways of preventing AOM through interventions at two different levels: by developing viral vaccines to prevent a healthy child from contracting the viral upper respiratory infection that precedes AOM and by coming up with antiviral drugs or bacterial vaccines to prevent a upper respiratory infection from evolving into AOM.
The same applies to pneumonia. Other investigators showed years ago that both respiratory viruses and bacteria were present in two-thirds of sputum samples obtained from children with community-acquired pneumonia (Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012 Mar;18[3]:300-7).
RSV is the top cause of hospitalization for acute respiratory infection – pneumonia and bronchiolitis – in infants. Worldwide, it’s estimated that RSV accounts for more than 33 million episodes of pneumonia annually, with 3.2 million hospitalizations and 118,200 deaths.
Beyond the hospital, however, Dr. Heikkinen and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study in Turku over the course of two consecutive respiratory infection seasons in which they captured the huge burden of RSV as an outpatient illness. It hit hardest in children younger than 3 years, in whom the average annual incidence of RSV infection was 275 cases per 1,000 children. In that youngest age population, RSV upper respiratory infection was followed by AOM 58% of the time, with antibiotics prescribed in 66% of the cases of this complication of RSV illness. The mean duration of RSV illness was greatest in this young age group, at 13 days, and it was associated with parental absenteeism from work at a rate of 136 days per 100 children with RSV illness.
Moreover, while AOM occurred less frequently in children aged 3-6 years, 46% of the cases were attributed to a preceding RSV infection, which led to antibiotic treatment nearly half of the time (J Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 1;215[1]:17-23). This documentation has spurred further efforts to develop RSV vaccines and antivirals.
Dr. Heikkinen was a cofounder of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Network (ReSViNET), an international collaborative group of researchers. He and other ReSViNET members have written a review article that outlines the new therapeutics in development (Lancet Respir Med. 2015 Nov;3[11]:888-900).
He reported serving as a consultant to a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies, as well as having received research funding from Janssen, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novavax.