Patients concerned about clinician burnout
Almost three-quarters of Americans are concerned about burnout among health care professionals, according to the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists.
The public is aware “that burnout among pharmacists, physicians, nurses, and other professionals can lead to impaired attention and decreased functioning that threatens to cause medical errors and reduce safety,” the ASHP said when it released data from a survey conducted May 28-30, 2019, by the Harris Poll.
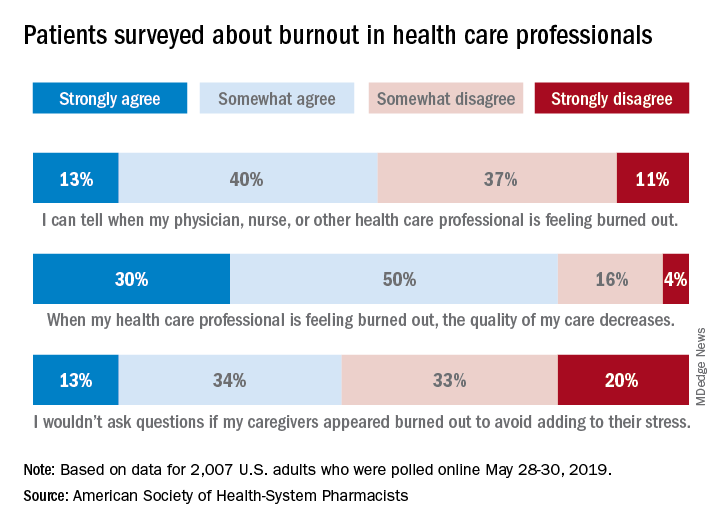
Those data show that 23% of respondents were very concerned and 51% were somewhat concerned about burnout among health care providers. Just over half (53%) of the 2,007 adults involved said that they could tell when a provider was burned out, suggesting that health care professionals “may be conveying signs of burnout to their patients without knowing it,” the society noted.
[embed:render:related:node:201865]
A majority of respondents (80%) felt that the quality of their care was affected when their physician, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care professional was burned out, and almost half (47%) said that they would avoid asking questions if their provider appeared burned out because they wouldn’t want to add to that person’s stress, the ASHP said.
“A healthy and thriving clinician workforce is essential to ensure optimal patient health outcomes and safety,” said Paul W. Abramowitz, PharmD, chief executive officer of the ASHP. “Within the healthcare industry, we are working to help build a culture of resilience and well-being to ensure that no patient or clinician is harmed due to burnout; but it takes a concerted effort from all entities involved – providers and healthcare organizations.”