Severe OSA increases cardiovascular risk after surgery
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
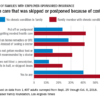
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.