CDC: Opioid prescribing and use rates down since 2010
Trends in opioid prescribing and use from 2010 to 2016 offer some encouragement, but opioid-attributable deaths continued to increase over that period, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Prescribing rates dropped during that period, as did daily opioid dosage rates and the percentage of patients with high daily opioid dosages, Gail K. Strickler, PhD, of the Institute for Behavioral Health at Brandeis University in Waltham, Mass., and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
Their analysis involved 11 of the 12 states (Washington was unable to provide data for the analysis) participating in the CDC’s Prescription Behavior Surveillance System, which uses data from the states’ prescription drug monitoring programs. The 11 states represented about 38% of the U.S. population in 2016.
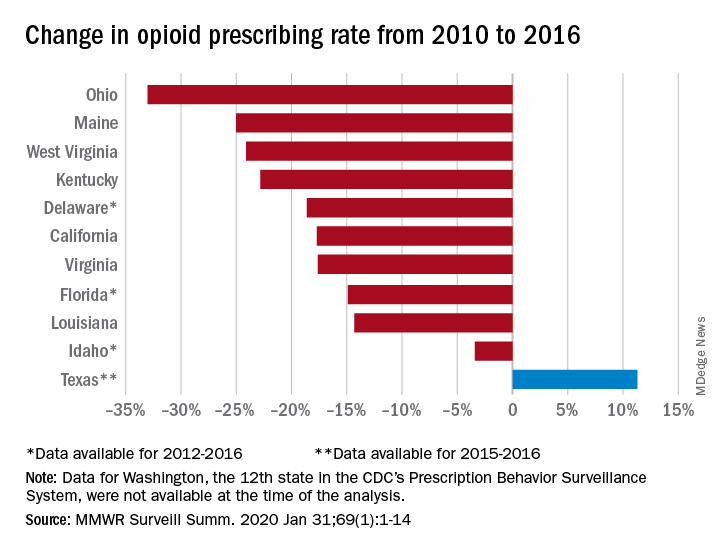
The opioid prescribing rate fell in 10 of those 11 states, with declines varying from 3.4% in Idaho to 33.0% in Ohio. Prescribing went up in Texas by 11.3%, but the state only had data available for 2015 and 2016. Three other states – Delaware, Florida, and Idaho – were limited to data from 2012 to 2016, the investigators noted.
Rural treatment of opioid use disorder increasingly driven by nonphysician workforce
As for the other measures, all states showed declines for the mean daily opioid dosage. Texas had the smallest drop at 2.9% and Florida saw the largest, at 27.4%. All states also had reductions in the percentage of patients with high daily opioid dosage, with decreases varying from 5.7% in Idaho to 43.9% in Louisiana, Dr. Strickler and associates reported. A high daily dosage was defined as at least 90 morphine milligram equivalents for all class II-V opioid drugs.
“Despite these favorable trends … opioid overdose deaths attributable to the most commonly prescribed opioids, the natural and semisynthetics (e.g., morphine and oxycodone), increased during 2010-2016,” they said.
It is possible that a change in mortality is lagging “behind changes in prescribing behaviors” or that “the trend in deaths related to these types of opioids has been driven by factors other than prescription opioid misuse rates, such as increasing mortality from heroin, which is frequently classified as morphine or found concomitantly with morphine postmortem, and a spike in deaths involving illicitly manufactured fentanyl combined with heroin and prescribed opioids since 2013,” the investigators suggested.
SOURCE: Strickler GK et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020 Jan 31;69(1):1-14.